-
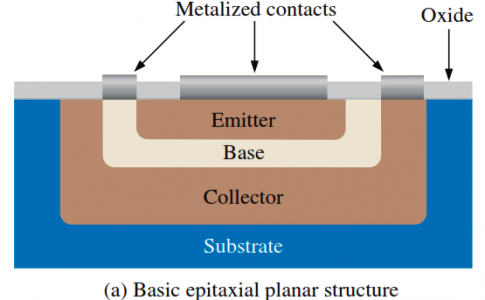
Bipolar Junction Transistor Construction
The basic structure of the bipolar junction transistor (BJT) determines its operating characteristics. The BJT is constructed with three doped ... -
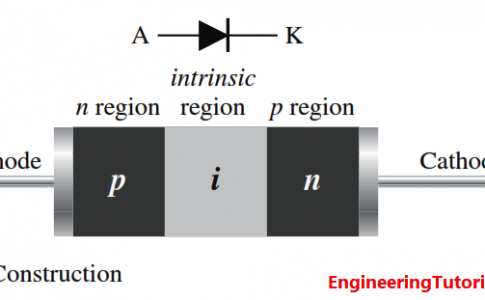
PIN Diode Working Principle
The pin diode consists of heavily doped p and n regions separated by an intrinsic (i) region, as shown in Figure ... -
Tunnel Diode Working Principle
A tunnel diode or Esaki diode is a type of semiconductor that is capable of very fast operation, well into ... -
Difference between Schottky Diode and PN junction Diode
Silicon diode: Use of P-doped silicon and N-doped silicon to make a P-N junction that causes the blocking effect Schokky ... -
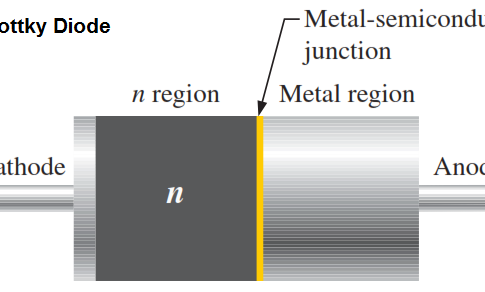
Schottky Diode Working Principle
What is a Schottky Diode? A Schottky diode, also known as a hot carrier diode, is a semiconductor diode which ... -
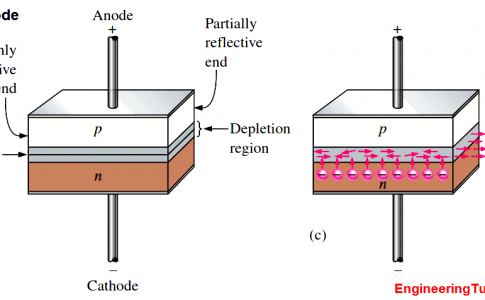
Laser Diode Working Principle
A laser diode, or LD also known as injection laser diode or ILD, is an electrically pumped semiconductor laser in ... -
Photodiode Working Principle
A photodiode is a semiconductor device that converts light into current. The current is generated when photons are absorbed in ... -
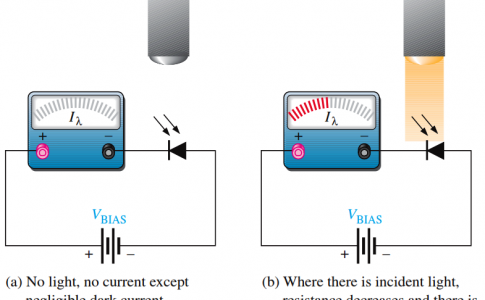
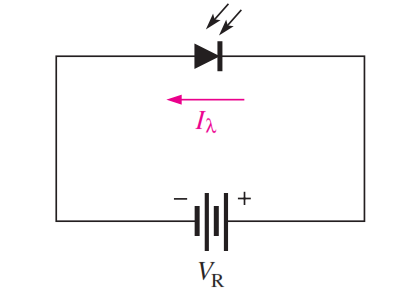
Photodiode as Variable Resistance Device
The photodiode is a device that operates in reverse bias, as shown in Figure. where Ia is the reverse light ... -
Limitations of Resistors
Over Heat Of Resistor Resistors are probably the most robust of all electronic components, with high reliability and a long ... -
Resistors Principle & Applications
A resistor is one of the most fundamental components in electronics. Its purpose is to impede a flow of current ...