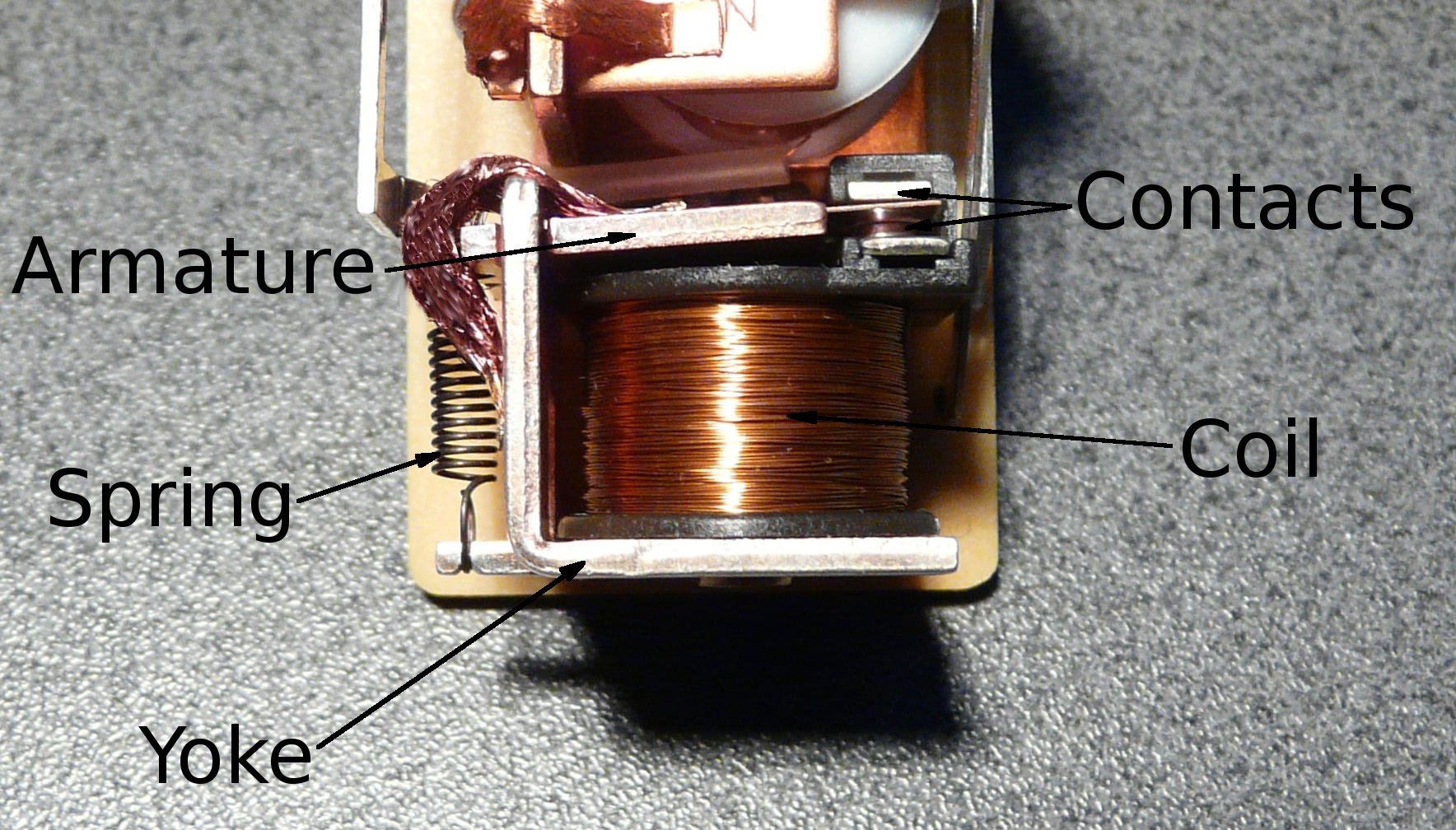
In Electromagnetic relays operating current flows through the coil. When this operating current increases, coil energizes the electromagnet. When the operating current becomes large, the magnetic field produced by electromagnet is high such that this magnetic field pulls the armature or plunger making the trip circuit contacts to close. Some of the advantages, disadvantages and applications of electromagnetic relays are explained below
Advantages or merits:
- Electromagnetic relays have fast operation and fast reset
- They can be used for both ac and dc systems for protection of ac and dc equipments
- Electromagnetic relays operating speeds which has the ability to operate in milliseconds are also can be possible
- They have the properties such as simple, robust, compact and most reliable
- These relays are almost instantaneous. Though instantaneous the operating time of the relay varies with the current. With extra arrangements like dashpot, copper rings etc. slow operating times and reset can be possible.
Disadvantages or demerits:
- High burden level instrument transformers are required (CTs and PTs of high burden is required for operating the electromagnetic relays compared to static relays)
- The directional feature is absent in electromagnetic relays
- Requires periodic maintenance and testing unlike static relays
- Relay operation can be affected due to ageing of the components and dust, pollution resulting in spurious trips
- Operation speed for an electromagnetic relays is limited by the mechanical inertia of the component
Applications:
- Electromagnetic relays are employed for the protection of various ac and dc equipments
- The over/under current and voltage protection of various ac and dc equipments
- For differential protection
- Used as auxiliary relays in the contact systems of protective relay schemes