What is protective relay?
It is an electrical device designed to initiate the isolation of a part of the electrical installation, or to operate an alarm signal, in the event of abnormal condition or a fault. In simple words relay is an electrical device that gives signal to isolation device (eg: Circuit Breaker) after sensing the fault and helps to isolate the fault system from the healthy electrical system.
What are the different relays that employed for protection of apparatus and transmission lines?
The relays that are usually employed for protection of transmission lines include
- Over current relay
- Directional relay
- Distance relay
- Under Voltage relay
- Under-frequency relay
- Thermal relay
- Differential relay
- Phase sequence relays
- pilot relays
How the electrical power system protection is divided?
The overall system protection is divided into
- Generator protection
- Transformer protection
- Busbar protection
- Transmission line protection and
- Feeder protection
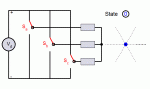
How relays are connected in the power system?
The relays are connected to the power system through the current transformer (CT) or potential transformer (PT).
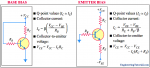
What are different types of principles of operation of electro-mechaical relays?
Eletro-mechanical relays operate by two principles. Electro-magnetic attraction and electro-magnetic induction. In electromagnetic attraction relay plunger is drawn to the solenoid or an armature is attracted to the poles of the electromagnet. In case of electro-magnetic induction, principle of operation is similar to induction motor. Torque is developed by electromagnetic induction principle.
Action carried out by the relay and circuit breaker during fault condition?
After the relay sensing the fault condition, relay operates and close the trip coils. The effect of this will be circuit breaker operate to open the contacts.
What is Relay Time?
Relay time is the interval between the occurrence of the fault and the closure of the relay contacts is called relay time.
What is fault clearance time?
When the fault occurs relay operates and close the trip coils and circuit breaker operates and open the contacts subsequently and fault is cleared. Therefore fault clearance time is the sum of relay operating time and circuit breaker operating time and clearing the fault
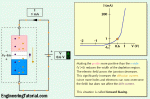
What is Reach?
Distance relay operates whenever the impedance seen (V/I) seen by the relay is less than the specified set value. This impedance or corresponding distance is known as reach of the relay. Reach is the limiting distance covered by the relay for protection of line. Faults beyond the distance (reach of the relay) relay will not operate and should be covered by the other relay.
What are the fundamental elements of relay?
Basic fundamental elements of the relay are:
- Sensing element: It is the measuring element measures the actuating quantity. Actuating quantity is change in current in case of over current relay
- Comparing element: It compares the actuating quantity with the relay pre-setting of the relay
- Control element: On pick up of the relay control element carryout the final switching operations such as closing the circuit to operate the circuit breaker
What are the good features of protective relaying?
Some of the good features for protective relaying are: Reliability, Selectivity, Sensitivity, Simplicity, Speed and economy
Some of the causes for relay failures?
Primary reason for relay failure to operate during faults are wrong settings, bad contacts and open circuit in the relay coil.